Biomanufacturing, or the manufacturing phase of innovative biological medicines, is a rapidly expanding field that is essential for meeting modern healthcare needs and represents a major strategic challenge. Faced with growing dependence on imports and increasing international competition, there are many technological and industrial challenges to developing this sector. In France, major efforts are being made, notably through the France 2030 plan, to ensure pharmaceutical sovereignty and meet future medical needs. This article explores the challenges and opportunities presented by biomanufacturing.
What is biomanufacturing?
Biomanufacturing refers to all the technical and industrial processes used for the large-scale production of complex biological molecules, such as therapeutic proteins, monoclonal antibodies or viral vectors for gene and cell therapy. Unlike traditional chemical drugs, biomedicines are produced from living systems such as mammalian cells, bacteria or yeast, generally genetically modified cells, grown in bioreactors under strictly controlled conditions.
This approach makes it possible to produce specific, effective treatments for a wide range of diseases, particularly in oncology, immunology and rare diseases. Biopharmaceuticals now account for a growing proportion of therapeutic innovations, with around 50% of clinical trials currently underway. However, biomanufacturing presents unique challenges in terms of complexity, cost and regulation. The often lengthy processes require rigorous control of numerous parameters to guarantee the quality and safety of the final product. Although the initial investment is often substantial compared with conventional production methods, it is nevertheless profitable in the long term once it has been scaled up.
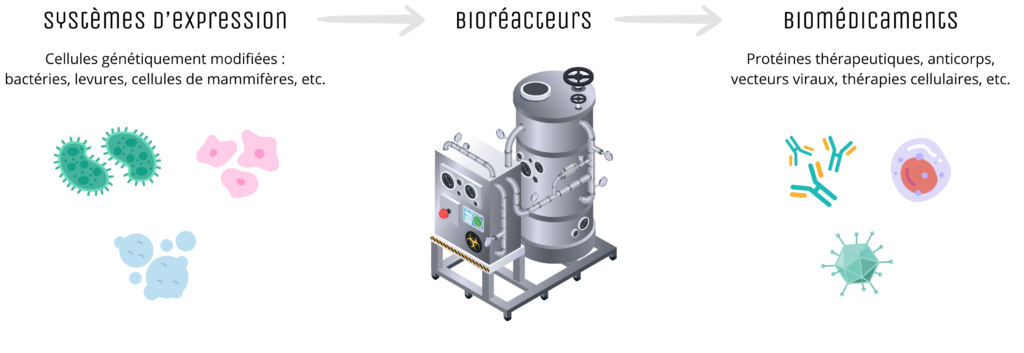
A simplified overview of bioproduction
Key issues in the biomanufacturing of biological drugs
The design of a biomedicine product begins with the identification of a therapeutic target and the selection of a biological molecule capable of interacting with this target. This stage often involves advanced molecular biology, protein engineering and bioinformatics techniques. Once the molecule has been designed, it is necessary to develop a cell line capable of producing it efficiently. This involves optimising the genetic sequences and selecting suitable host cells, generally mammalian cells such as CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells.
The development of robust analytical methods is crucial for characterising biomedicines at every stage of their production. These methods are used to verify the identity, purity and biological activity of the product. The techniques used include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, capillary electrophoresis and various immunological methods. The challenge is to develop methods that are sufficiently sensitive and specific to detect the slightest variations in the structure or composition of the biomedicine product.
The use of mathematical models and numerical simulations is becoming increasingly important in the optimisation of bioproduction processes. Digital twins’ are detailed virtual representations of production systems that can be used to predict and optimise bioreactor performance. These tools help to reduce development time and costs by enabling different culture conditions and production strategies to be explored virtually. They also help to improve understanding of the complex biological processes involved in bioproduction.
The ‘developability’ of biomedicines, also known as biologics, refers to the ability to produce a molecule on a large scale, efficiently and economically, while retaining its therapeutic properties. This concept encompasses several aspects:
- The stability of the molecule during production, storage and administration
- Solubility and tendency to aggregate
- Ease of purification
- Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics
Assessing and optimising developability at the earliest stages of design is essential to avoid costly problems during the subsequent development and production phases.
The production of biomedicines is subject to strict regulations to guarantee the safety and efficacy of the products. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) must be rigorously followed throughout the production process. The concept of Quality by Design (QbD) is increasingly being adopted in the biopharmaceutical industry. This approach aims to integrate quality right from the product and process design stage, by identifying critical quality attributes and controlling critical process parameters. Regulatory authorities, such as France’s Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé (ANSM), the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), require comprehensive documentation on all aspects of production, including product characterisation, process validation and in-process controls.
Future strategic challenges for the biomanufacturing sector
2020: the turning point in the Covid-19 pandemic
The Covid-19 pandemic marked a turning point for biomanufacturing, suddenly highlighting its strategic importance and the vulnerabilities of global pharmaceutical supply chains. The race to develop and produce messenger RNA vaccines demonstrated the biopharmaceutical industry’s capacity for innovation and rapid adaptation. However, this crisis has also revealed the dependence of many countries, including France, on imports of essential biological products. For example, 97% of monoclonal antibodies prescribed in France are produced abroad. This situation has led to a collective realisation of the need to strengthen national and European biomanufacturing capacities, not only for vaccines, but for all biomedicines.
Global bioproduction capacity
The global biomanufacturing market is growing rapidly, driven by increasing demand for biomedicines and the emergence of new innovative therapies such as gene and cell therapies. In the United States and Canada, the biomanufacturing industry is mature and benefits from a dynamic innovation ecosystem, with numerous biotech companies and significant production capacity.
In Europe, although certain countries such as Germany and Switzerland have a strong presence in this sector, the region as a whole is seeking to strengthen its capacities in order to reduce its dependence on imports.
Asia, particularly China and South Korea, is investing massively in bioproduction, with the construction of numerous high-capacity facilities and production costs that are often lower than in Europe and the United States.
Against this backdrop, France faces a number of challenges in positioning itself as a major player:
- Accelerating the development of its production capacity
- Investing in training and attracting talent
- Supporting innovation in bioproduction technologies
- Create a favourable regulatory and fiscal environment for investment in this sector
In France, vaccine production is the most developed biomanufacturing activity, representing more than 8,500 jobs. However, the country faces a number of challenges, not least a lack of intermediaries between the major pharmaceutical groups and biotech companies, which are mainly start-ups.
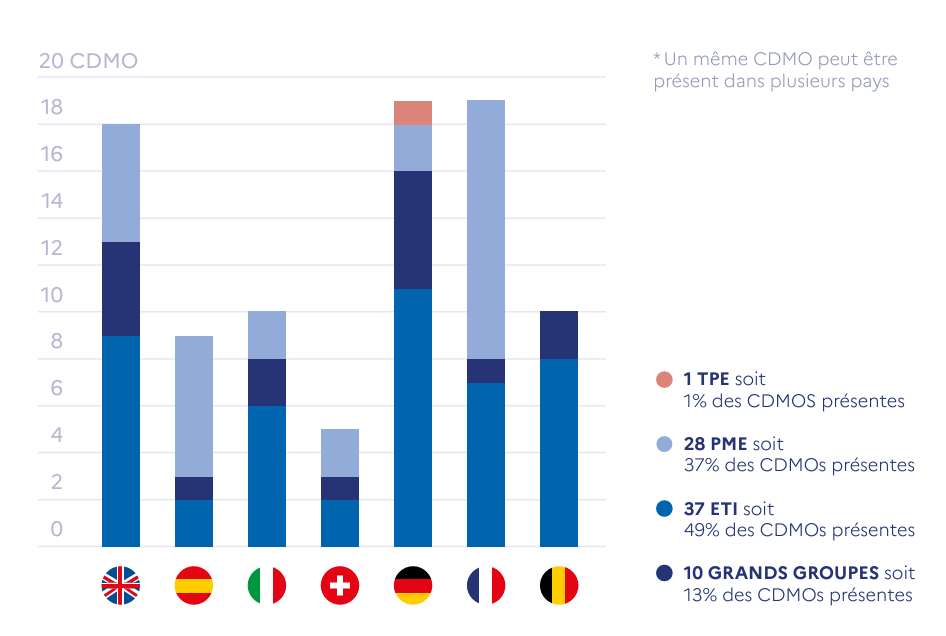
CDMO landscape in Europe – From the study and characterisation of the biomedicine sector in France, France 2030 (see sources)

Production sites – Taken from the study and characterisation of the biomedicine sector in France, France 2030 (see sources)
France 2030, an investment plan and a major sovereignty issue

Faced with these challenges, the French government launched the ‘France 2030’ plan in 2021, which includes a major section dedicated to biomanufacturing. The plan aims to make France a European leader in this strategic field by 2030. The main objectives of this plan are:
- Significantly increase national production capacity
- Supporting innovation in bioproduction technologies
- Train the talent needed for this fast-growing industry
- Making France a more attractive place to invest in this sector
The plan provides for massive investment, in particular through the ‘Grand Défi Biomédicaments’, which supports public-private consortia working on key innovations such as :
- The development of advanced management tools for bioproduction lines
- The creation of innovative robotic systems to improve flexibility and safety in the factories of the future
- Developing new biological systems to produce the biomedicines of tomorrow
These initiatives aim to reduce production costs, increase yields and improve the quality of biomedical products, while guaranteeing patient safety.
What players are needed to develop and produce biomedical products in France?
The biomanufacturing landscape in France is made up of various players:
- Research institutes and universities: they contribute to innovation and the training of future experts in biomanufacturing.
- Biotechs: these innovative companies, often spin-offs from academic research, play a crucial role in the development of new biological molecules.
- Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs): these specialist companies offer development and production services on behalf of other companies.
- Large pharmaceutical companies: they have the resources needed to carry out large-scale biomanufacturing projects.
Collaboration between these different players is essential to create a dynamic and competitive ecosystem.
Communication and events to boost the biomanufacturing sector
To stimulate the development of the bioproduction sector in France, a number of communication and event initiatives have been put in place:
- Sector directory: A collaborative tool called ‘MyBiologicsPartner’, launched in 2024 by LEEM, France BioLead and MabDesign, lists the players in the French biomanufacturing sector and aims to highlight the expertise of the companies in the network and make it easier for players in the sector to find partners.
- Conferences and trade fairs: These events enable industry players to meet, discuss the latest advances and forge partnerships. MabDesign organises its annual Bioproduction Congress.
- Training programs: Initiatives are being launched to train future biomanufacturing professionals and meet the growing need for skilled labour. MabDesign offers targeted biomanufacturing training at all levels.
- Awareness campaigns: Efforts are being made to inform the general public about the importance of biomedical products and biomanufacturing for public health.
- Collaboration platforms: Initiatives are being put in place to facilitate collaboration between the various players in the ecosystem (businesses, research laboratories, public institutions).

Conclusion
Biomanufacturing represents a major strategic challenge for France and Europe, in terms of both public health and economic independence. The challenges are numerous, ranging from technological innovation to talent training, not to mention the establishment of an appropriate regulatory framework.
The France 2030 plan and related initiatives demonstrate the political will to position France as a leader in this crucial area. However, the success of this ambition will depend on the country’s ability to mobilise its resources effectively, foster collaboration between public research and industry, and adapt rapidly to technological developments and market needs.
The stakes are high: not only do we need to ensure that French and European patients have access to innovative treatments that are increasingly personalised to meet the specific needs of individual patients, but we also need to create a cutting-edge industry that generates skilled jobs and added value for the national economy.
Don’t miss the 10th Bioproduction Congress (BIOPC2025), organised by MabDesign, to be held in Lyon on 22 and 23 September 2025. The biotherapy industry will be discussing the future of biomanufacturing, current challenges and the latest innovations.
If you have a project involving biomanufacturing or, more broadly, biomedicines, don’t hesitate to take a look at our range of services and get in touch with us for a chat. We will be delighted to put our expertise to work to help you achieve your goals.
To stay at the cutting edge of knowledge and innovation, take a look at our bioproduction training courses.
Sources
- MabDesign expertise and data
- Bioproduction de protéines thérapeutiques : Revue et perspectives. Med Sci (Paris) 2009 ; 25 : 18–26
- Revue des bioproductions de santé en France. Tanguy Lemasson. Sciences pharmaceutiques (2022)
- Le Monde – La France tente de combler son retard dans les biomédicaments (17/06/2024)
- BioProcessWatch Analytical tools in bioprocessing. 2023 Edition MabDesign
- Investir dans la France 2030 : devenir un leader de la production de thérapies innovantes. Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche, Communiqué de presse (07/01/2022
- Study and characterisation of the biomedicine sector in France. Study carried out in 2023 by Mabdesign for France 2030, the Agence de l’innovation en santé and its Biomedicaments et Bioproduction en thérapies innovantes acceleration strategy, France Biotech and France Biolead.